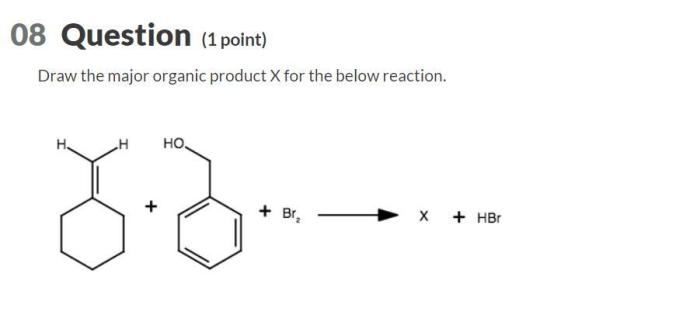
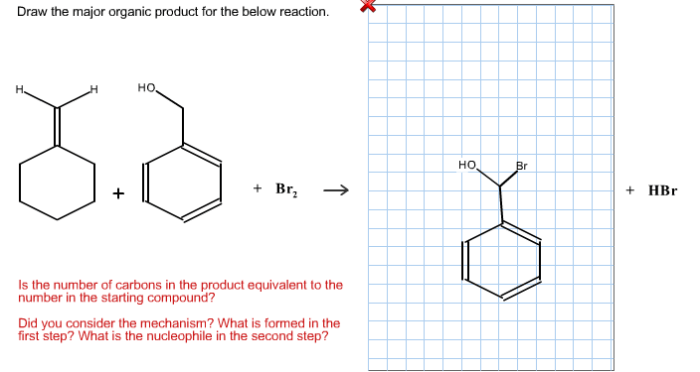
Draw the major organic product x for the below reaction – In the realm of organic chemistry, predicting the outcome of reactions is a crucial skill. One of the most fundamental aspects of this endeavor is the ability to identify the major organic product formed in a given reaction. This article delves into the intricacies of drawing the major organic product, providing a comprehensive guide to understanding the factors that govern its formation.
The process of drawing the major organic product involves a multi-faceted approach that encompasses identifying functional groups, determining reaction mechanisms, analyzing reaction conditions, and illustrating the reaction pathway. By mastering these concepts, chemists can develop a deep understanding of organic reactions and make accurate predictions about their outcomes.
Organic Reactions: A Comprehensive Guide
Organic reactions are chemical processes that involve the transformation of organic compounds into new organic compounds. These reactions play a crucial role in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, polymers, and other important materials.
To understand and predict the outcome of an organic reaction, it is essential to have a deep understanding of the fundamental concepts and principles involved. This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of the key aspects of organic reactions, including identifying functional groups, determining reaction mechanisms, predicting the major organic product, analyzing reaction conditions, and illustrating the reaction pathway.
1. Identifying Functional Groups
The first step in understanding an organic reaction is to identify the functional groups present in the reactants. Functional groups are specific arrangements of atoms that impart characteristic chemical properties to organic compounds.
Some common functional groups include:
- Alkanes (C-H)
- Alkenes (C=C)
- Alkynes (C≡C)
- Alcohols (C-OH)
- Aldehydes (C=O)
- Ketones (C=O)
- Carboxylic acids (COOH)
- Amines (NH2)
Identifying the functional groups present in the reactants is important because it allows us to predict the types of reactions that are likely to occur.
2. Determining the Reaction Mechanism, Draw the major organic product x for the below reaction
Once the functional groups have been identified, the next step is to determine the reaction mechanism. A reaction mechanism is a detailed description of the steps involved in an organic reaction, including the formation and breaking of bonds.
There are two main types of reaction mechanisms:
- Homolytic reactions: Reactions in which bonds are broken and formed homolytically, meaning that each atom takes one of the electrons in the bond.
- Heterolytic reactions: Reactions in which bonds are broken and formed heterolytically, meaning that one atom takes both electrons in the bond.
The type of reaction mechanism that occurs depends on the nature of the reactants and the reaction conditions.
3. Predicting the Major Organic Product
Once the reaction mechanism has been determined, the next step is to predict the major organic product. The major organic product is the product that is formed in the greatest yield.
There are two main factors that influence the formation of the major organic product:
- Regioselectivity: The regioselectivity of a reaction refers to the preference for one regioisomer over another.
- Stereoselectivity: The stereoselectivity of a reaction refers to the preference for one stereoisomer over another.
Predicting the major organic product can be challenging, but it is an essential skill for organic chemists.
Answers to Common Questions: Draw The Major Organic Product X For The Below Reaction
What is the significance of identifying functional groups in organic reactions?
Functional groups are the reactive centers of organic molecules, and their identification is essential for understanding the reaction mechanisms and predicting the products formed.
How does the reaction mechanism influence the major organic product?
The reaction mechanism determines the pathway by which the reactants are transformed into products. Different mechanisms can lead to different major products, so it is crucial to identify the most likely mechanism for a given reaction.
What factors influence the formation of the major organic product?
Factors such as regioselectivity, stereoselectivity, temperature, solvent, and catalysts can all impact the formation of the major organic product.