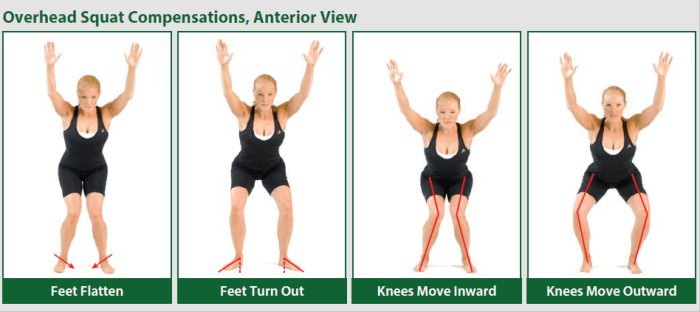
What depth is suggested for the overhead squat assessment – The overhead squat assessment is a valuable tool for evaluating lower body mobility, stability, and strength. Determining the appropriate depth for this assessment is crucial to ensure accurate results and minimize the risk of injury. This article explores the recommended depth for the overhead squat assessment, considering individual variations and safety considerations.
The overhead squat assessment involves holding a weight overhead while squatting. The depth of the squat is measured as the angle between the thigh and the calf at the bottom of the movement. Research suggests that a depth of approximately 90 degrees, where the thighs are parallel to the floor, is generally recommended for the overhead squat assessment.
Assessment Overview: What Depth Is Suggested For The Overhead Squat Assessment

The overhead squat assessment is a functional movement test that assesses an individual’s mobility, stability, and coordination. It is commonly used to evaluate lower body mechanics, core strength, and overall athleticism.
The assessment is performed by having the individual stand with their feet shoulder-width apart and holding a weight overhead. They then squat down until their thighs are parallel to the floor, before returning to the starting position.
There are a number of different factors that can affect the depth of the squat, including height, weight, mobility, and fitness level. As such, it is important to individualize the assessment based on the specific needs of the individual.
Depth Recommendations
There is no one-size-fits-all answer to the question of how deep to squat. However, there are some general recommendations that can be used as a starting point.
- For most people, a depth of around parallel to the floor is a good starting point.
- Individuals with good mobility and flexibility may be able to squat deeper, while those with limited mobility may need to squat shallower.
- It is important to avoid squatting too deep, as this can put excessive stress on the knees and lower back.
- It is also important to avoid squatting too shallow, as this can reduce the effectiveness of the exercise.
Individual Variations, What depth is suggested for the overhead squat assessment
As mentioned above, there are a number of individual factors that can influence the optimal depth for the overhead squat. These factors include:
- Height:Taller individuals will typically need to squat deeper than shorter individuals in order to achieve the same range of motion.
- Weight:Heavier individuals will typically need to squat shallower than lighter individuals in order to maintain proper form.
- Mobility:Individuals with limited mobility in the hips, knees, or ankles may need to squat shallower than those with good mobility.
- Fitness level:Individuals with higher fitness levels will typically be able to squat deeper than those with lower fitness levels.
It is important to take these factors into account when determining the optimal depth for the overhead squat.
Safety Considerations
The overhead squat assessment is a relatively safe exercise, but there are some safety considerations that should be kept in mind.
- Use a spotter:When performing the overhead squat with a weight, it is important to have a spotter present to help you in case you lose your balance.
- Warm up properly:Before performing the overhead squat, it is important to warm up your muscles and joints. This will help to reduce the risk of injury.
- Listen to your body:If you experience any pain during the overhead squat, stop the exercise and consult with a medical professional.
User Queries
Why is it important to determine the appropriate depth for the overhead squat assessment?
Determining the appropriate depth for the overhead squat assessment is important to ensure accurate results and minimize the risk of injury. Squatting too deep can strain the knees, while squatting too shallow may not provide an adequate assessment of lower body mobility and strength.
How do individual factors influence the optimal depth for the overhead squat?
Individual factors such as height, weight, mobility, and fitness level can influence the optimal depth for the overhead squat. Taller individuals with longer limbs may need to squat deeper to reach the recommended 90-degree angle, while shorter individuals with shorter limbs may need to squat shallower.
What are the safety considerations associated with the overhead squat assessment?
The overhead squat assessment should be performed with proper form and technique to minimize the risk of injury. This includes maintaining a neutral spine, keeping the knees aligned with the toes, and avoiding excessive weight. It is recommended to consult with a qualified professional before performing the overhead squat assessment, especially if you have any underlying health conditions or injuries.