The figure below shows the supply curve for tennis balls, a graphical representation that captures the relationship between the price of tennis balls and the quantity supplied by producers. This curve serves as a crucial tool for understanding market dynamics and predicting supply-side behavior.
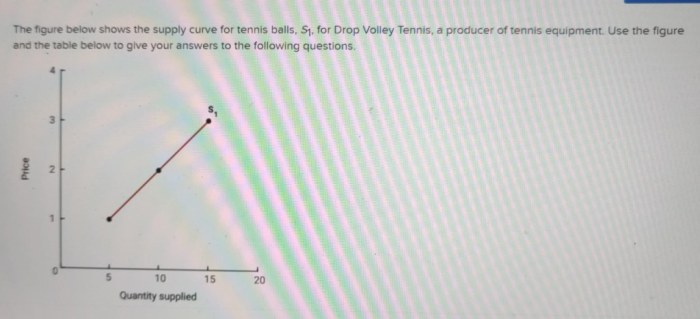
The supply curve depicts an upward-sloping line, indicating that as the price of tennis balls increases, producers are willing to supply a greater quantity. This relationship stems from the profit-maximizing motive of firms, who respond to higher prices by increasing production to capture a larger share of the market.
Supply Curve Definition
A supply curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity that producers are willing and able to supply at that price. It is a fundamental tool in economics, used to analyze market behavior and predict supply-side responses to changes in market conditions.
The shape and position of a supply curve are influenced by various factors, including production costs, technology, the availability of resources, and expectations about future prices.
Interpretation of the Figure
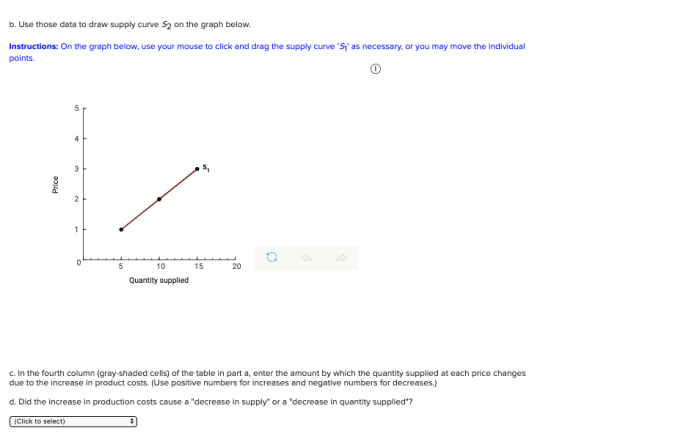
The figure shows the supply curve for tennis balls. The vertical axis represents the price of tennis balls, while the horizontal axis represents the quantity supplied. The curve slopes upward, indicating that as the price of tennis balls increases, producers are willing and able to supply a larger quantity.
Elasticity of Supply
The elasticity of supply measures the responsiveness of quantity supplied to changes in price. It is calculated as the percentage change in quantity supplied divided by the percentage change in price.
Using the data provided in the figure, we can calculate the elasticity of supply as follows:
- When the price increases from $10 to $12, the quantity supplied increases from 100,000 to 120,000 units.
- Percentage change in price = (12-10)/10 – 100% = 20%
- Percentage change in quantity supplied = (120,000-100,000)/100,000 – 100% = 20%
- Elasticity of supply = Percentage change in quantity supplied / Percentage change in price = 20% / 20% = 1
An elasticity of supply of 1 indicates that the quantity supplied is perfectly elastic. This means that producers can easily increase or decrease their output in response to changes in price.
Shifts in the Supply Curve: The Figure Below Shows The Supply Curve For Tennis Balls
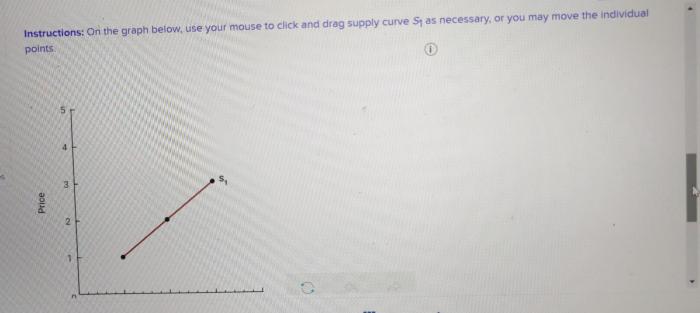
The supply curve can shift for various reasons, including:
- Changes in production costs
- Changes in technology
- Changes in the availability of resources
- Changes in expectations about future prices
For example, if the cost of producing tennis balls increases, the supply curve will shift to the left, indicating that producers are willing and able to supply a smaller quantity at any given price.
Market Equilibrium
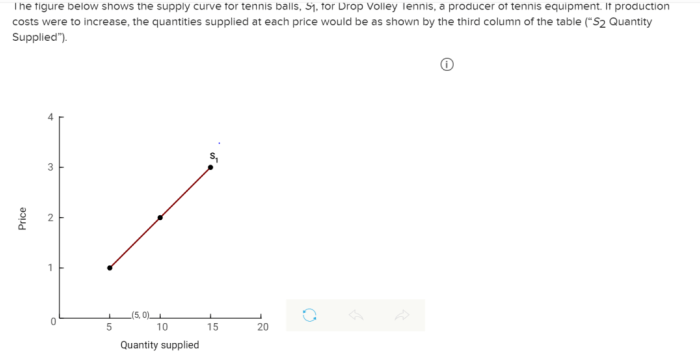
Market equilibrium is the point where the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded. In the figure, the equilibrium price is $10 and the equilibrium quantity is 100,000 units.
Factors that could disrupt market equilibrium include changes in supply or demand. For example, if the cost of producing tennis balls increases, the supply curve will shift to the left, leading to a new equilibrium price and quantity.
FAQ Resource
What is the significance of the supply curve?
The supply curve is a graphical representation that depicts the relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity supplied by producers. It helps economists understand how changes in price affect the willingness of producers to supply goods and services.
How does elasticity of supply affect market equilibrium?
Elasticity of supply measures the responsiveness of producers to changes in price. A highly elastic supply curve indicates that producers can easily adjust their production levels in response to price changes, while an inelastic supply curve indicates that production levels are less responsive to price changes.
This elasticity affects the stability of market equilibrium and the extent to which prices and quantities adjust to changes in market conditions.
What factors can cause the supply curve to shift?
The supply curve can shift due to changes in factors such as production costs, technology, government policies, and natural disasters. For example, an increase in production costs can lead to a leftward shift in the supply curve, while a technological advancement that reduces production costs can lead to a rightward shift.