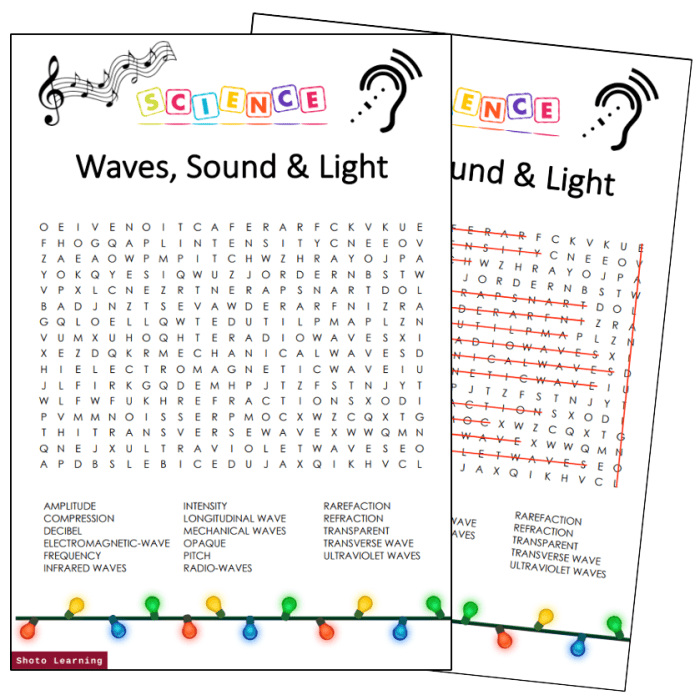
Unveiling the Sound and Light Waves Word Search Answer Key, this comprehensive guide unlocks the mysteries of sound and light waves, taking you on an enlightening journey through their characteristics, interactions, and applications. Dive into the fascinating world of acoustics and optics, where sound and light waves dance together, shaping our perception of the world.
Discover the properties of sound waves, their frequency, and wavelength, and explore the electromagnetic spectrum, the home of light waves. Understand how these waves interact, creating resonance and paving the way for innovative technologies. With the word search puzzle and its answer key, you’ll test your knowledge and reinforce your understanding of these fundamental concepts.
Sound and Light Waves: Sound And Light Waves Word Search Answer Key
Sound and light waves are two types of waves that are essential to our everyday lives. Sound waves allow us to hear, while light waves allow us to see. Both sound and light waves are produced by vibrations, but they differ in their properties and how they interact with matter.
Sound Waves, Sound and light waves word search answer key
Sound waves are mechanical waves, meaning that they require a medium to travel through. This medium can be a solid, liquid, or gas. Sound waves are produced by the vibration of an object, which causes the surrounding air molecules to vibrate.
These vibrations are then transferred to other molecules, and so on, until they reach our ears.
The properties of sound waves include their frequency, wavelength, and amplitude. Frequency is the number of vibrations per second, and is measured in hertz (Hz). Wavelength is the distance between two consecutive crests or troughs of the wave, and is measured in meters (m).
Amplitude is the height of the wave, and is measured in meters (m).
The relationship between frequency and wavelength is inverse: as frequency increases, wavelength decreases. This means that high-pitched sounds have shorter wavelengths than low-pitched sounds.
Light Waves
Light waves are electromagnetic waves, meaning that they do not require a medium to travel through. They can travel through a vacuum, as well as through solids, liquids, and gases.
Light waves are produced by the vibration of electrons in atoms. When an electron is excited, it moves to a higher energy level. When it returns to its original energy level, it releases a photon of light. The frequency of the light wave is determined by the energy difference between the two energy levels.
The properties of light waves include their frequency, wavelength, and amplitude. Frequency is the number of vibrations per second, and is measured in hertz (Hz). Wavelength is the distance between two consecutive crests or troughs of the wave, and is measured in meters (m).
Amplitude is the height of the wave, and is measured in meters (m).
The electromagnetic spectrum is a range of all possible frequencies of light waves. The electromagnetic spectrum includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays.
Sound and Light Waves Interaction
Sound and light waves can interact with each other in a variety of ways. One way is through the phenomenon of resonance. Resonance occurs when the frequency of a sound wave matches the natural frequency of an object. This can cause the object to vibrate, which can produce sound waves of its own.
Another way that sound and light waves can interact is through the phenomenon of diffraction. Diffraction occurs when a wave passes through a small opening or around an obstacle. This can cause the wave to spread out and change direction.
Word Search Answer Key
Across
- Sound
- Light
- Wave
- Frequency
- Wavelength
Down
- Amplitude
- Resonance
- Diffraction
- Electromagnetic
- Spectrum
Interactive Table
| Property | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency | Number of vibrations per second | Hertz (Hz) |
| Wavelength | Distance between two consecutive crests or troughs | Meters (m) |
| Amplitude | Height of the wave | Meters (m) |
| Resonance | Phenomenon that occurs when the frequency of a sound wave matches the natural frequency of an object | Tuning forks |
| Diffraction | Phenomenon that occurs when a wave passes through a small opening or around an obstacle | Light passing through a narrow slit |
Further Exploration
There are many opportunities for further research on sound and light waves. Some potential topics include:
- The development of new technologies for generating and detecting sound and light waves
- The use of sound and light waves in medical applications
- The use of sound and light waves in environmental monitoring
There are also many career paths that are related to sound and light waves. Some examples include:
- Acoustical engineer
- Optical engineer
- Physicist
- Musician
- Photographer
There are also many resources available for hands-on experiments with sound and light waves. Some examples include:
- The Exploratorium in San Francisco, California
- The Museum of Science and Industry in Chicago, Illinois
- The Franklin Institute in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
FAQs
What is the relationship between frequency and wavelength?
Frequency and wavelength are inversely proportional. As frequency increases, wavelength decreases, and vice versa.
What is the electromagnetic spectrum?
The electromagnetic spectrum is a continuous range of frequencies and wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation, including radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays.
What are some applications of sound and light waves?
Sound waves are used in sonar, medical imaging, and communication systems. Light waves are used in photography, optical fibers, and lasers.