Embark on an enlightening journey with acids and bases crossword answers, where the intricate world of chemical interactions unfolds before your eyes. Prepare to delve into the fundamental concepts, explore their captivating properties, and unravel the mysteries that lie at the heart of these essential substances.
From the groundbreaking theories of Arrhenius, Brønsted-Lowry, and Lewis to the practical applications that shape our daily lives, this exploration promises a comprehensive understanding of acids and bases, leaving you with a profound appreciation for their significance in the world of science and beyond.
Acids and Bases: Acids And Bases Crossword Answers
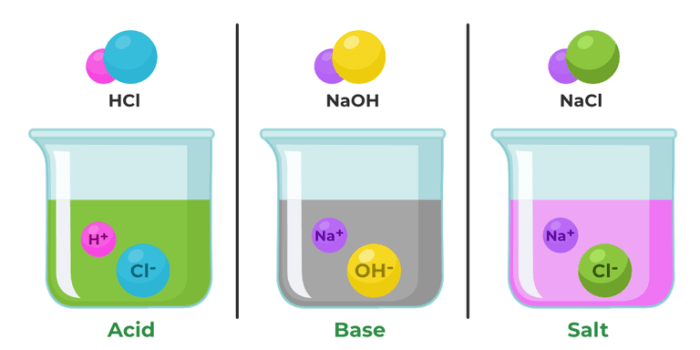
Acids and bases are two important classes of chemical compounds that play a vital role in many chemical reactions. They are defined by their properties and their ability to react with each other.
Acid-Base Definitions
According to the Arrhenius theory, acids are substances that produce hydrogen ions (H+) when dissolved in water, while bases are substances that produce hydroxide ions (OH-) when dissolved in water.
The Brønsted-Lowry theory defines acids as proton donors and bases as proton acceptors. A proton is a hydrogen ion (H+). According to this theory, an acid-base reaction is a proton transfer reaction.
The Lewis theory defines acids as electron-pair acceptors and bases as electron-pair donors. According to this theory, an acid-base reaction is an electron-pair transfer reaction.
Acid-Base Properties
Acids have a sour taste, can react with metals to produce hydrogen gas, and turn blue litmus paper red.
Bases have a bitter taste, can react with acids to produce water, and turn red litmus paper blue.
Common examples of acids include hydrochloric acid (HCl), sulfuric acid (H2SO4), and nitric acid (HNO3). Common examples of bases include sodium hydroxide (NaOH), potassium hydroxide (KOH), and calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2).
Acid-Base Reactions
When an acid and a base react, they undergo a neutralization reaction. In this reaction, the hydrogen ions from the acid combine with the hydroxide ions from the base to form water. The products of an acid-base reaction are always a salt and water.
For example, when hydrochloric acid (HCl) reacts with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), the products are sodium chloride (NaCl) and water (H2O).
Acid-Base Strength, Acids and bases crossword answers
The strength of an acid or base is determined by its ability to donate or accept protons. Strong acids donate protons easily, while weak acids donate protons less easily. Strong bases accept protons easily, while weak bases accept protons less easily.
The strength of an acid or base is also affected by its concentration. The higher the concentration of an acid or base, the stronger it is.
Examples of strong acids include hydrochloric acid (HCl), sulfuric acid (H2SO4), and nitric acid (HNO3). Examples of weak acids include acetic acid (CH3COOH) and carbonic acid (H2CO3). Examples of strong bases include sodium hydroxide (NaOH), potassium hydroxide (KOH), and calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2).
Examples of weak bases include ammonia (NH3) and pyridine (C5H5N).
Clarifying Questions
What is the difference between an acid and a base?
Acids release hydrogen ions (H+) in water, while bases release hydroxide ions (OH-) in water.
What is the pH scale?
The pH scale measures the acidity or basicity of a solution, ranging from 0 (highly acidic) to 14 (highly basic).
What are buffers?
Buffers are solutions that resist changes in pH when small amounts of acid or base are added.