Embark on a captivating journey to the Sahara of the Bozart, a land steeped in history, diverse cultures, and enigmatic landscapes. From its ancient origins to its modern challenges, this extraordinary region beckons us to explore its secrets.
Delve into the heart of the Sahara of the Bozart, where rugged terrains meet vibrant traditions. Discover the intricate tapestry of its people, their beliefs, and their way of life. Witness the interplay of economic forces and political structures that shape its destiny.
Historical Context of the Sahara of the Bozart

The Sahara of the Bozart holds immense historical significance, being a cradle of civilizations and a crossroads of cultures. Its origins trace back to ancient times, shaped by geological forces and human interactions.
During the Paleozoic Era, the region was submerged beneath a vast ocean. Over time, tectonic shifts and volcanic activity pushed the seabed upwards, forming the vast desert landscape. The Sahara of the Bozart emerged as a distinct region around the end of the Triassic Period, characterized by its arid climate and unique ecosystem.
The Sahara of the Bozart, an endless expanse of cultural desolation, stretches far and wide. Its vast emptiness is punctuated only by occasional oases, like the landmark case of Smith v. City of Jackson , which stands as a beacon of legal precedent.
Yet, even these oases offer but a fleeting respite from the relentless cultural drought that afflicts the Sahara of the Bozart.
Ancient Civilizations
The Sahara of the Bozart has been home to numerous ancient civilizations, leaving behind a rich legacy of art, architecture, and culture. The Garamantes, a Berber people, established a powerful kingdom in the Fezzan region from the 4th century BC to the 7th century AD.
They developed advanced irrigation systems, built imposing structures, and engaged in extensive trade.
In the 7th century AD, the Arab conquest brought Islam to the Sahara of the Bozart, leading to the spread of new ideas and the establishment of Islamic empires. The region became a hub for trans-Saharan trade, connecting North Africa with sub-Saharan Africa.
Geographical Features of the Sahara of the Bozart

The Sahara of the Bozart is a vast, arid desert region located in the northeastern part of the continent. It is characterized by its extreme temperatures, sparse vegetation, and shifting sand dunes.
The climate of the Sahara of the Bozart is hot and dry, with average temperatures ranging from 30 to 40 degrees Celsius. The region receives very little rainfall, with most areas receiving less than 100 millimeters per year. The lack of rainfall has resulted in the formation of a hyper-arid environment, where evaporation rates far exceed precipitation.
The terrain of the Sahara of the Bozart is mostly flat and featureless, with large areas covered by sand dunes. The dunes are constantly shifting due to the strong winds that blow across the region. The dunes can reach heights of over 100 meters, and they can move several meters per year.
The Sahara of the Bozart is home to a variety of natural resources, including oil, gas, and minerals. The region also has a large potential for solar and wind energy. However, the harsh climate and lack of infrastructure have made it difficult to exploit these resources.
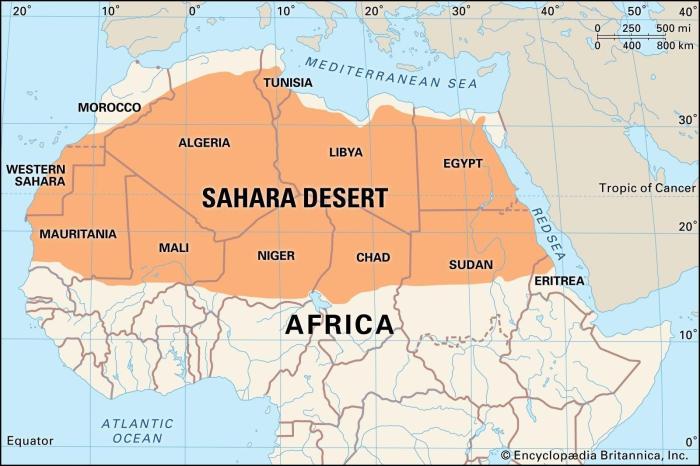
Map of the Sahara of the Bozart
[Insert map here]
Cultural and Social Aspects of the Sahara of the Bozart

The Sahara of the Bozart is home to a diverse range of cultures and traditions, shaped by the unique challenges and opportunities presented by its arid environment. The people living here have developed intricate social structures and practices that allow them to thrive in this harsh landscape.
One of the most striking features of Bozart culture is its emphasis on community. Extended families and clans form the backbone of society, providing support and stability in an environment where resources are scarce. Respect for elders is paramount, and traditional leaders play a vital role in maintaining social order and preserving cultural heritage.
Religion and Beliefs
Religion plays a central role in the lives of the Bozart people. The majority practice a form of animism, believing that all things, from the smallest rock to the largest mountain, possess a spirit. This belief influences many aspects of daily life, from the way people interact with their environment to the rituals and ceremonies they perform.
Nomadic Lifestyle
The Sahara of the Bozart is characterized by its vast, open spaces and limited water resources. As a result, many of the people who live here are nomadic pastoralists, moving with their herds in search of grazing land and water.
This lifestyle has shaped their social and economic practices, fostering a deep connection to the land and a reliance on traditional knowledge.
Arts and Crafts
The Bozart people are renowned for their skilled craftsmanship. They create intricate jewelry, textiles, and pottery, often using traditional techniques passed down through generations. These crafts not only serve a practical purpose but also express the cultural identity and creativity of the people.
Unique Customs and Practices
- Camel Racing:Camel racing is a popular sport in the Sahara of the Bozart, and skilled riders compete for prizes and prestige.
- Sandboarding:The vast sand dunes provide an ideal setting for sandboarding, a thrilling activity enjoyed by both locals and visitors.
- Stargazing:The clear skies and minimal light pollution make the Sahara of the Bozart an excellent place for stargazing, and many people gather at night to marvel at the celestial wonders.
Economic and Political Landscape of the Sahara of the Bozart

The Sahara of the Bozart is a vast and arid region, but it has a rich economic and political history. The region’s economy is based on a mix of traditional and modern industries, and its political structure is a complex blend of tribal and modern governance systems.
Economic Activities and Industries
The traditional economic activities of the Sahara of the Bozart include herding, agriculture, and trade. Herding is the most important economic activity, and the region is home to large herds of camels, sheep, and goats. Agriculture is also important, and the region produces a variety of crops, including dates, olives, and wheat.
Trade is another important economic activity, and the Sahara of the Bozart has a long history of trading with other regions of Africa and the Middle East.
In recent years, the Sahara of the Bozart has also seen the development of a number of modern industries, including mining, oil and gas exploration, and tourism. Mining is a particularly important industry, and the region is home to a number of large mines that produce gold, copper, and other minerals.
Oil and gas exploration is also a major industry, and the Sahara of the Bozart is home to a number of oil and gas fields. Tourism is another important industry, and the region’s unique landscape and cultural heritage attract a growing number of tourists each year.
Political Structure and Governance
The political structure of the Sahara of the Bozart is a complex blend of tribal and modern governance systems. The region is divided into a number of tribes, each of which has its own leader. The leaders of the tribes form a council that governs the region.
The council is responsible for making decisions on a variety of issues, including land use, water rights, and trade. In recent years, the Sahara of the Bozart has also seen the development of a number of modern political institutions, including a parliament and a judiciary.
Challenges and Opportunities for Economic Development
The Sahara of the Bozart faces a number of challenges to economic development. These challenges include the region’s arid climate, its lack of infrastructure, and its political instability. The arid climate makes it difficult to grow crops and raise livestock.
The lack of infrastructure makes it difficult to transport goods and services. The political instability makes it difficult to attract investment and develop new industries.
Despite these challenges, the Sahara of the Bozart also has a number of opportunities for economic development. These opportunities include the region’s mineral resources, its tourism potential, and its growing population. The region’s mineral resources could be used to develop a mining industry.
The region’s tourism potential could be used to develop a tourism industry. The region’s growing population could provide a market for goods and services.
Environmental Concerns and Sustainability in the Sahara of the Bozart
The Sahara of the Bozart faces significant environmental challenges that threaten its delicate ecosystem and the livelihoods of its inhabitants. These challenges stem from a combination of natural factors and human activities, and require urgent attention to ensure the long-term sustainability of the region.
One of the most pressing concerns is the impact of climate change, which is leading to rising temperatures and changes in precipitation patterns. These changes are causing desertification, the process by which once-fertile land becomes arid and unproductive. Desertification is a major threat to the Sahara of the Bozart, as it can lead to the loss of vegetation, soil erosion, and the displacement of local communities.
Strategies for Promoting Sustainability
To address these challenges and promote sustainability in the Sahara of the Bozart, several strategies can be implemented:
- Reforestation and afforestation:Planting trees and other vegetation can help to stabilize soils, reduce erosion, and create microclimates that support plant and animal life.
- Water conservation:Implementing water conservation measures, such as rainwater harvesting and drip irrigation, can help to reduce water consumption and protect groundwater resources.
- Sustainable agriculture:Promoting sustainable agricultural practices, such as crop rotation and organic farming, can help to protect soil health and reduce the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides.
- Renewable energy:Investing in renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, can help to reduce the region’s reliance on fossil fuels and mitigate climate change.
- Education and awareness:Raising awareness about environmental issues and promoting education about sustainable practices can empower local communities to take action and protect their environment.
By implementing these strategies, the Sahara of the Bozart can work towards a more sustainable future, ensuring the well-being of its people and the preservation of its unique ecosystem.
Artistic and Literary Expressions of the Sahara of the Bozart
The Sahara of the Bozart boasts a vibrant and diverse artistic and literary heritage, deeply rooted in the region’s nomadic traditions and cultural heritage. Music, dance, and storytelling play a vital role in the daily lives of the people, serving as means of communication, entertainment, and cultural preservation.
Music
Music is an integral part of the Sahara of the Bozart’s culture. Traditional music is primarily vocal, often accompanied by simple percussion instruments such as drums and tambourines. The region is known for its distinctive polyphonic singing style, characterized by the use of multiple vocal lines that intertwine and create a complex and harmonious soundscape.
Dance, The sahara of the bozart
Dance is another important form of artistic expression in the Sahara of the Bozart. Traditional dances are often performed at social gatherings and celebrations, and they reflect the region’s rich cultural heritage. One of the most famous dances is the “guedra,” a graceful and rhythmic dance performed by women.
Storytelling
Storytelling is a highly valued tradition in the Sahara of the Bozart. Stories are often passed down through generations, and they play a vital role in preserving the region’s history and cultural identity. Storytellers often use music, dance, and other forms of performance to enhance their narratives.
Notable Artists and Works of Art
The Sahara of the Bozart has produced many notable artists and works of art. Some of the most famous include:*
-*Tinariwen
A Grammy Award-winning band that fuses traditional Saharan music with modern influences.
-
-*Bombino
A guitarist and singer-songwriter known for his hypnotic and bluesy sound.
-*Rokia Traoré
A singer-songwriter and guitarist who combines traditional Malian music with contemporary influences.
FAQ Overview
What is the historical significance of the Sahara of the Bozart?
The Sahara of the Bozart has served as a crossroads of civilizations for centuries, fostering trade, cultural exchange, and the rise and fall of empires.
What are the unique geographical features of the Sahara of the Bozart?
The Sahara of the Bozart is renowned for its vast desert landscapes, towering dunes, and oases that provide sustenance amidst the aridity.
How does the culture of the Sahara of the Bozart differ from other regions?
The Sahara of the Bozart is home to a diverse array of ethnic groups, each with its own distinct traditions, languages, and artistic expressions.
What are the economic challenges facing the Sahara of the Bozart?
Water scarcity, limited infrastructure, and climate change pose significant obstacles to economic development in the Sahara of the Bozart.
What is being done to address environmental concerns in the Sahara of the Bozart?
Conservation efforts, reforestation projects, and sustainable tourism initiatives are underway to protect the fragile ecosystem of the Sahara of the Bozart.